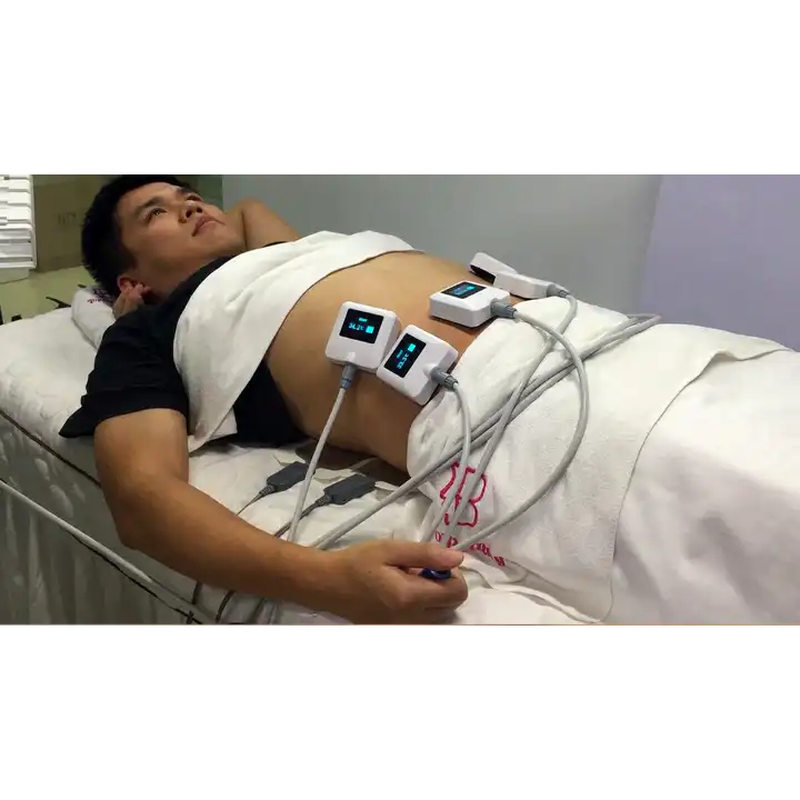
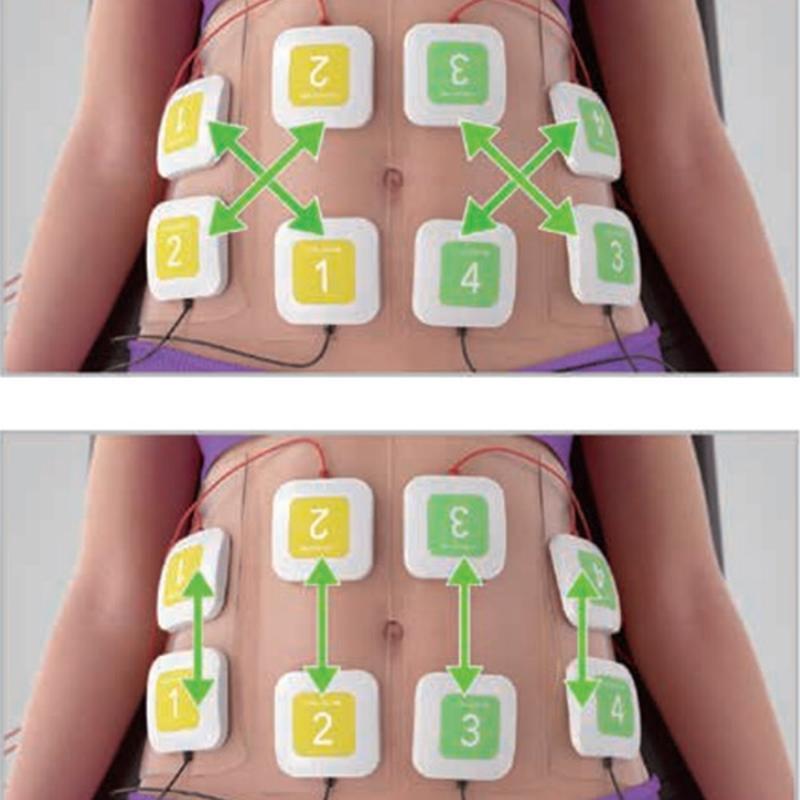
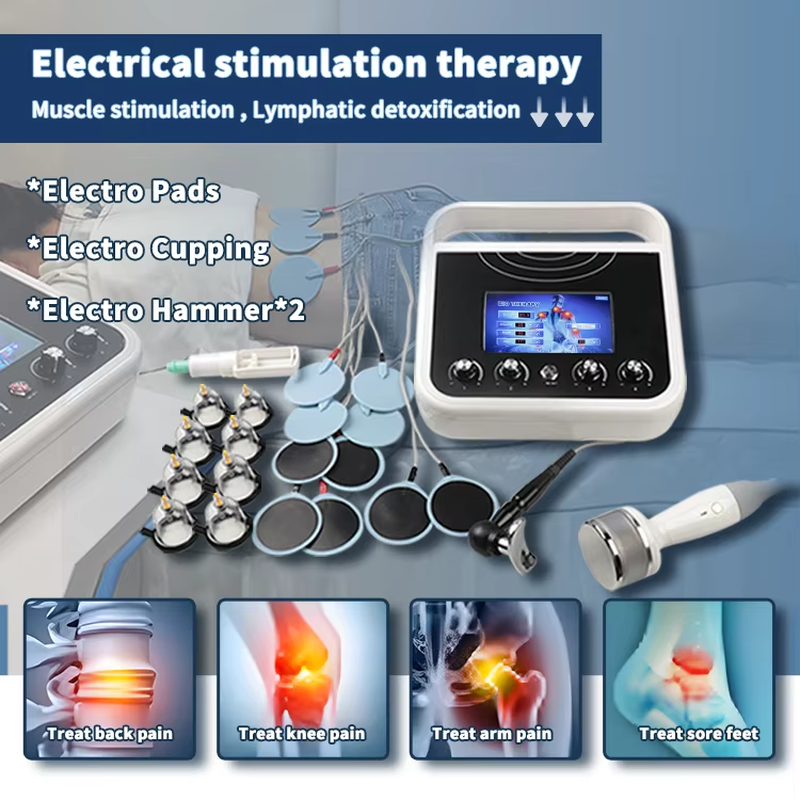
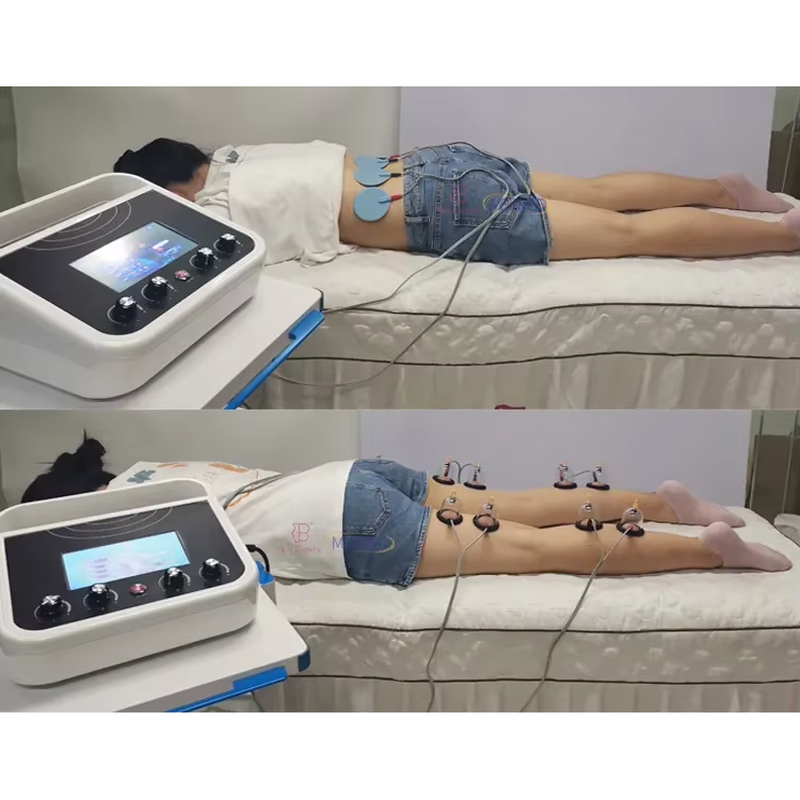
EMS Therapy (Electrical Muscle Stimulation Therapy) is a technique that uses electrical impulses to stimulate muscle contractions, mimicking the natural signals sent by the nervous system.
EMS Therapy
EMS Therapy (Electrical Muscle Stimulation Therapy) is a technique that uses electrical impulses to stimulate muscle contractions, mimicking the natural signals sent by the nervous system. Here’s a breakdown of its key aspects:
-
Definition & Mechanism
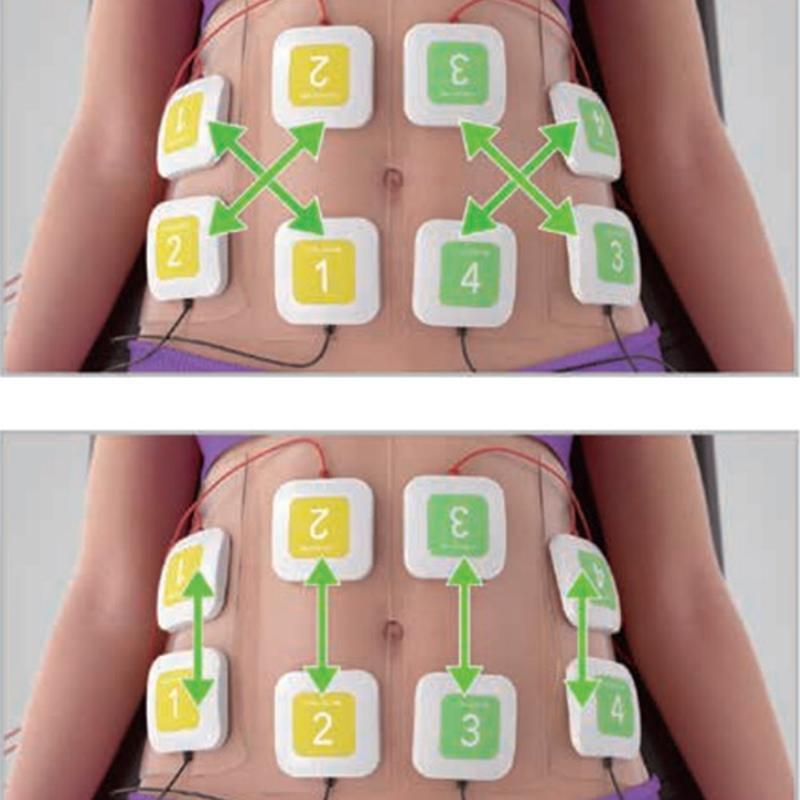
EMS delivers low-frequency electrical currents via electrodes placed on the skin, directly targeting motor neurons to induce muscle contractions. This bypasses the brain’s signals, allowing passive muscle activation. -
Applications
- Rehabilitation: Used post-injury or surgery to prevent muscle atrophy (e.g., stroke recovery, ACL rehabilitation).
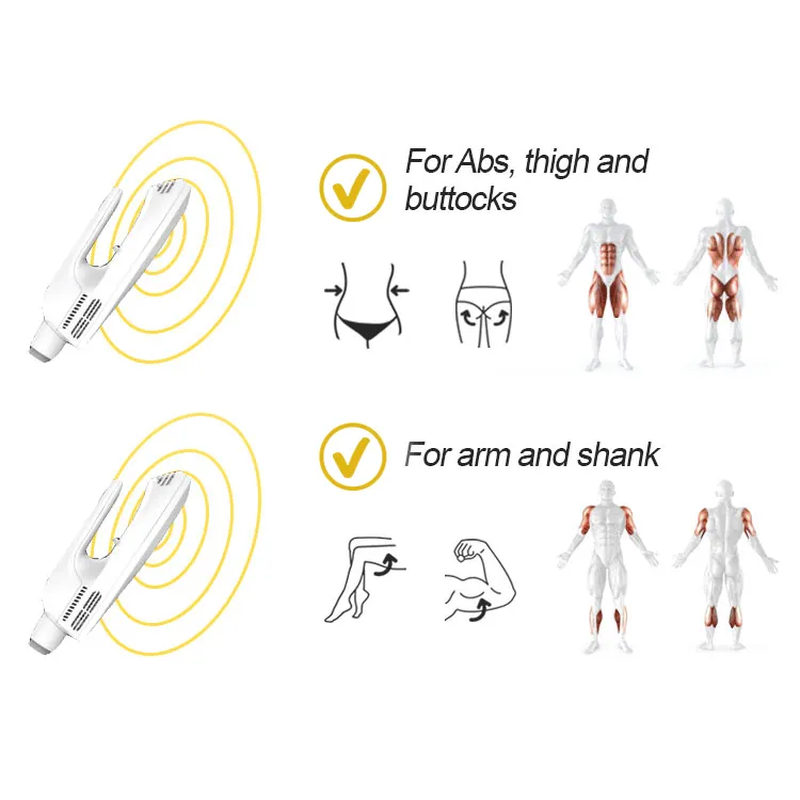
- Fitness & Athletics: Enhances strength and endurance by recruiting more muscle fibers than voluntary contractions alone. Athletes like Usain Bolt have used EMS for training.
- Pain Relief: Some devices (e.g., TENS) overlap with EMS technology to alleviate pain by disrupting pain signals.
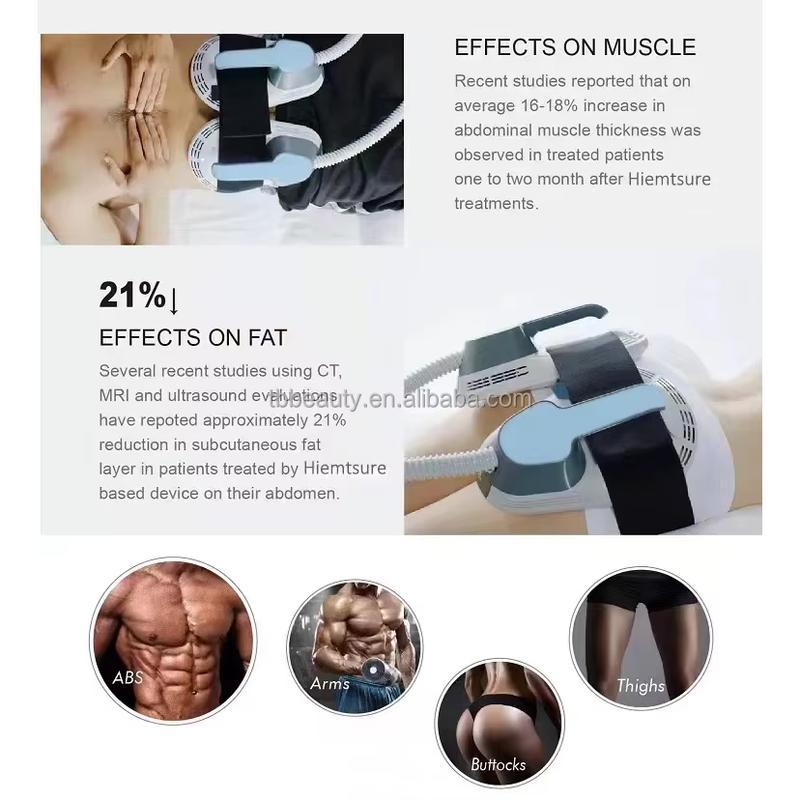
- Aesthetic/Wellness: Claims include muscle toning and "passive exercise," though FDA notes it’s not a standalone weight-loss tool.
-
Types & Variations
- Russian Stimulation: Uses high-frequency sine waves for deeper muscle penetration.
- NMES (Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation): Focuses on rehabilitating nerve-damaged muscles.
- Microcurrent (MS): Lower-intensity currents (under 500μA) for facial rejuvenation and ATP production, differing from EMS’s higher-intensity muscle contractions.
-
Safety & Limitations
- Contraindications: Not recommended for pregnant individuals, pacemaker users, or those with acute infections/epilepsy.
- Effectiveness: Best results require active participation (e.g., combining EMS with traditional exercise). Overuse may deplete ATP, leading to muscle fatigue.
-
Historical Context
Originating from 18th-century experiments by Galvani, EMS gained prominence in 20th-century space programs (NASA) to combat zero-gravity muscle loss.
For specific uses (e.g., rehab vs. fitness), consult a professional to tailor parameters like frequency and intensity.