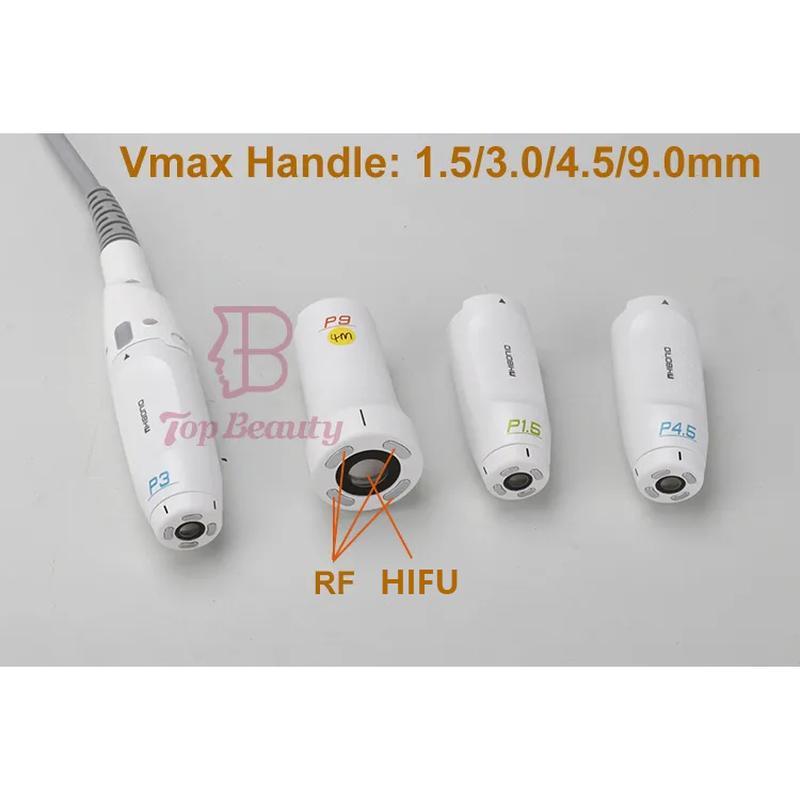
Ultrasonic Therapy is a form of physical therapy that utilizes high - frequency sound waves to treat various medical conditions.
Ultrasonic Therapy
Ultrasonic Therapy is a form of physical therapy that utilizes high - frequency sound waves to treat various medical conditions. Here is a detailed overview:
Basic Principle
- Ultrasonic waves are sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper limit of human hearing (above 20,000 Hz). In Ultrasonic Therapy, these waves are generated by a transducer, which converts electrical energy into mechanical vibrations. When the ultrasonic waves are applied to the body, they cause a series of mechanical and thermal effects. The mechanical effects include vibration, rotation, and streaming of the tissue fluids, which can promote the movement of molecules and enhance cellular metabolism. The thermal effect is due to the conversion of ultrasonic energy into heat as the waves are absorbed by the tissues, which can increase blood circulation and promote the repair of damaged tissues.
Types of Ultrasonic Therapy
- Continuous - wave Ultrasonic Therapy: In this mode, the ultrasonic waves are emitted continuously at a constant frequency and intensity. It is often used to produce a relatively uniform heating effect in the tissues, which is beneficial for treating chronic inflammations and promoting tissue healing.
- Pulsed - wave Ultrasonic Therapy: Here, the ultrasonic waves are emitted in short pulses with intervals between them. This type is used when a more targeted and less intense effect is desired. Pulsed - wave ultrasonic therapy can stimulate cell activity and tissue regeneration without causing excessive heating, making it suitable for treating certain soft - tissue injuries and bone fractures.
Medical Applications
- Musculoskeletal Disorders: Ultrasonic Therapy is widely used to treat conditions such as tendonitis, bursitis, muscle strains, and joint pain. The heat and mechanical effects of the ultrasonic waves can reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and improve the flexibility of the affected joints and muscles. For example, it is often used in the treatment of tennis elbow, where it helps to break down scar tissue and promote the healing of damaged tendons.
- Wound Healing: It can accelerate the healing process of chronic wounds and ulcers. The ultrasonic waves enhance the migration and proliferation of fibroblasts, which are essential cells for wound repair. They also improve blood circulation in the wound area, bringing more oxygen and nutrients to support tissue regeneration.
- Neurological Conditions: In some cases, Ultrasonic Therapy is used to treat neurological disorders. It has been shown to have a positive effect on nerve regeneration and can help relieve symptoms such as nerve pain and muscle spasms. For example, it may be used in the rehabilitation of patients with peripheral nerve injuries.
Advantages
- Non - Invasive: Ultrasonic Therapy is a non - invasive treatment method, which means it does not require surgery or the use of needles. This reduces the risk of complications and side effects associated with invasive procedures, making it a relatively safe option for many patients.
- Targeted Treatment: The ultrasonic waves can be precisely focused on the affected area, allowing for a targeted treatment. This enables the therapist to deliver the therapeutic effects directly to the site of the problem while minimizing the impact on surrounding healthy tissues.
- Versatile: It can be used to treat a wide range of medical conditions, from musculoskeletal problems to skin and neurological disorders. Its versatility makes it a valuable tool in the field of physical medicine and rehabilitation.
Disadvantages and Risks
- Overheating: If the ultrasonic energy is not properly controlled, it can cause overheating of the tissues, which may lead to burns or other thermal injuries. This is especially a concern when treating areas close to the skin surface or in tissues that are more sensitive to heat.
- Limited Penetration Depth: The penetration depth of ultrasonic waves in the body is limited. Deeper - seated tissues may not receive the full therapeutic effect, and the effectiveness of the treatment may be reduced for conditions located far from the skin surface.
- Contraindications: Ultrasonic Therapy is not suitable for all patients. It is contraindicated in areas with active infections, tumors, or over areas with metal implants, as the ultrasonic waves can interact with the metal and cause unpredictable effects. Pregnant women should also avoid ultrasonic treatment on the abdomen and lower back to prevent potential harm to the fetus.