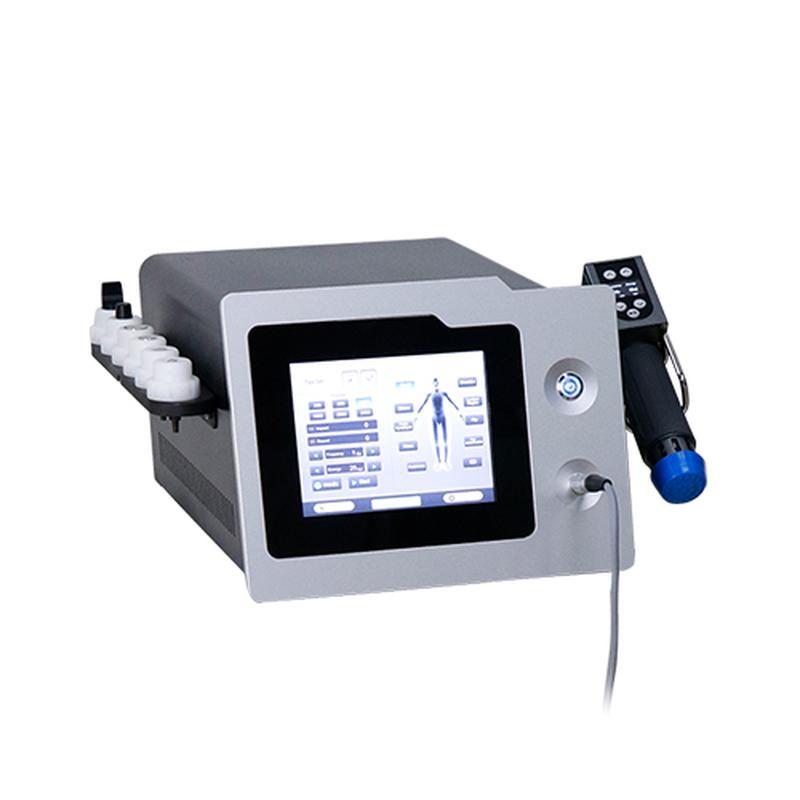
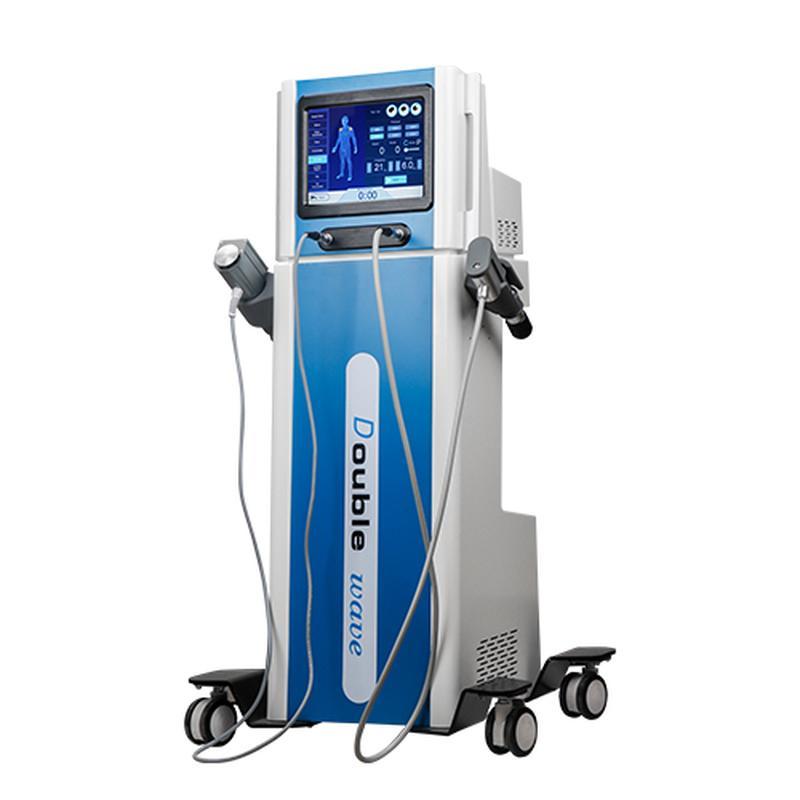
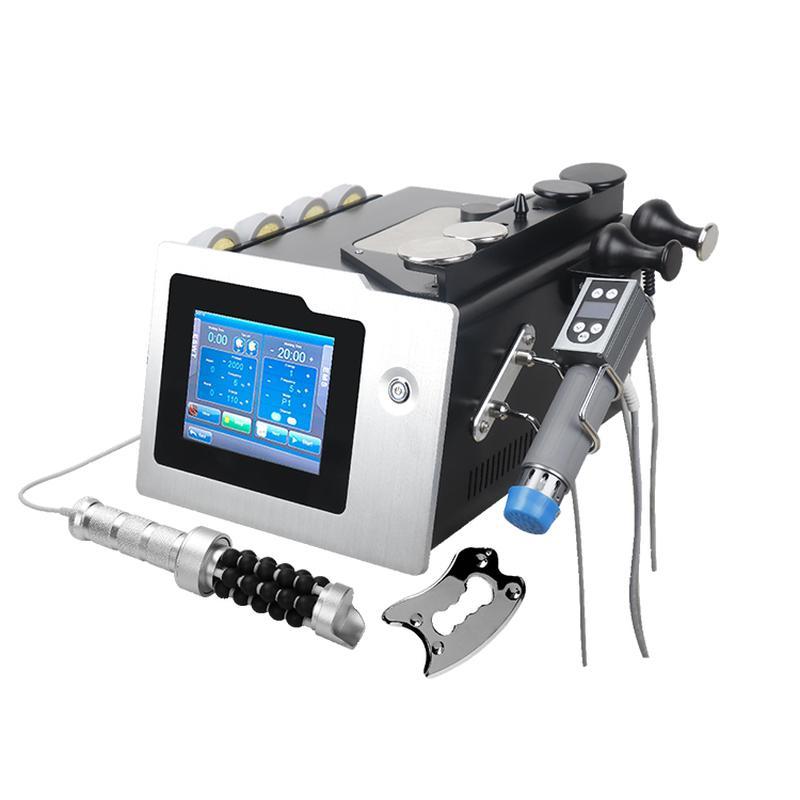
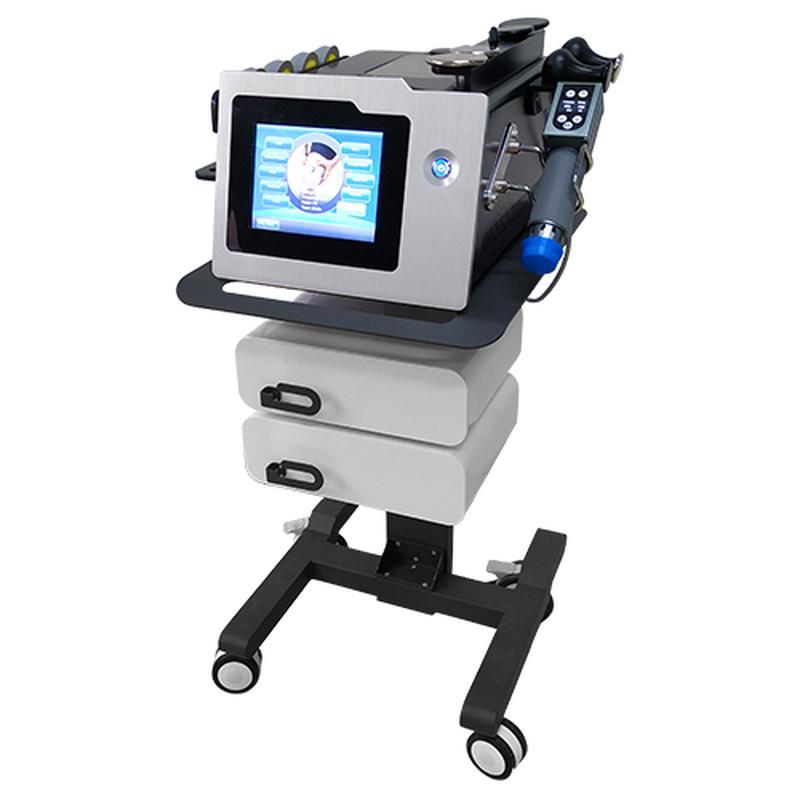
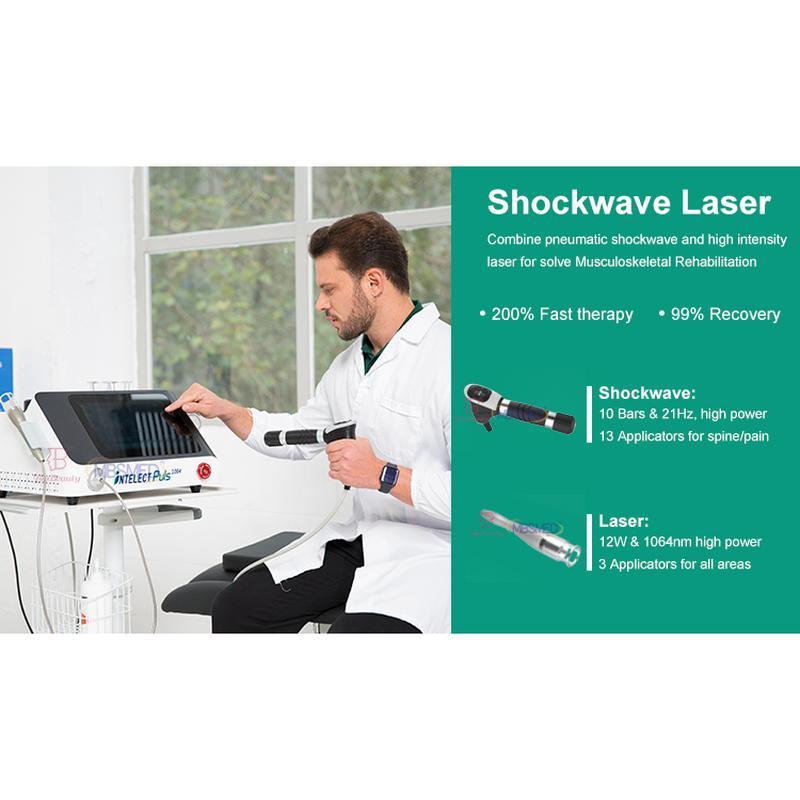
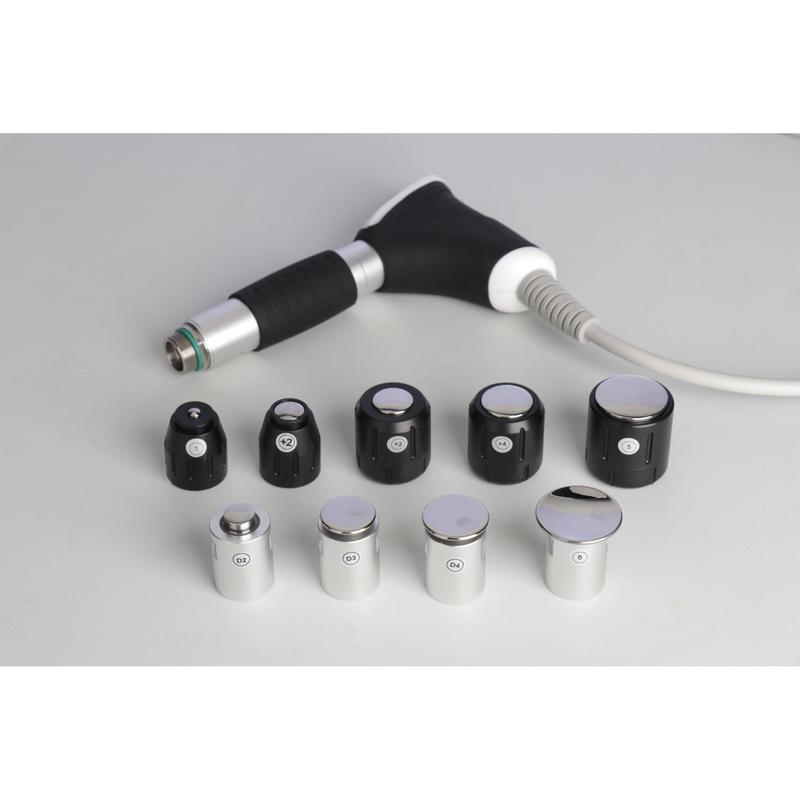
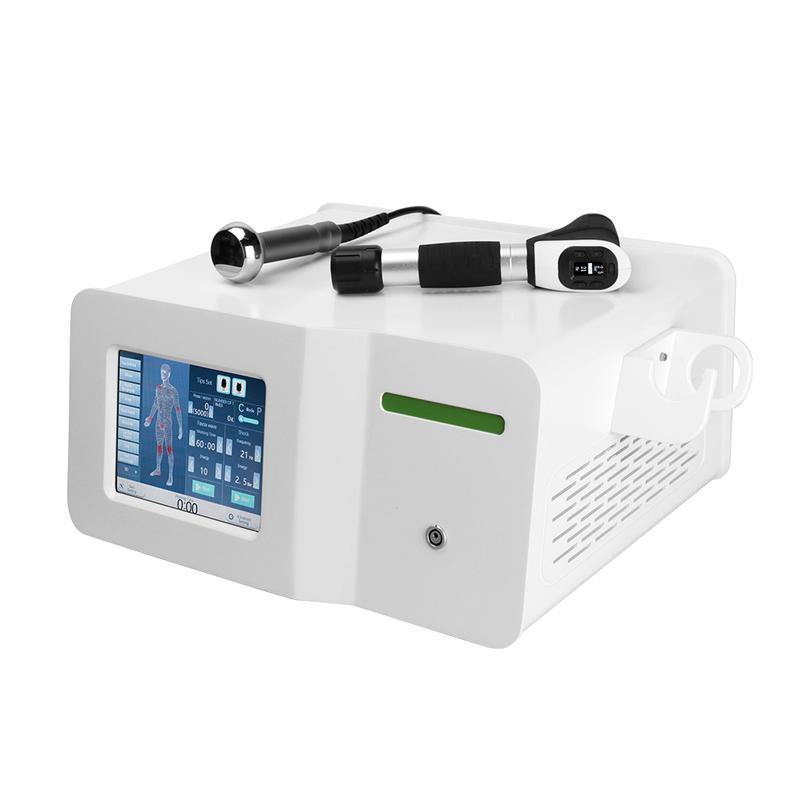
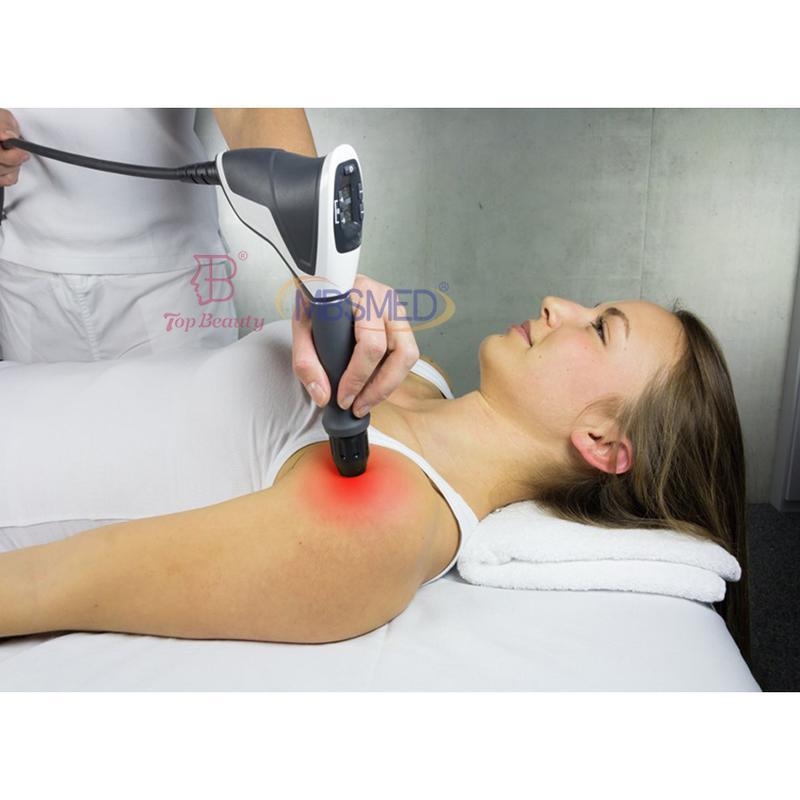
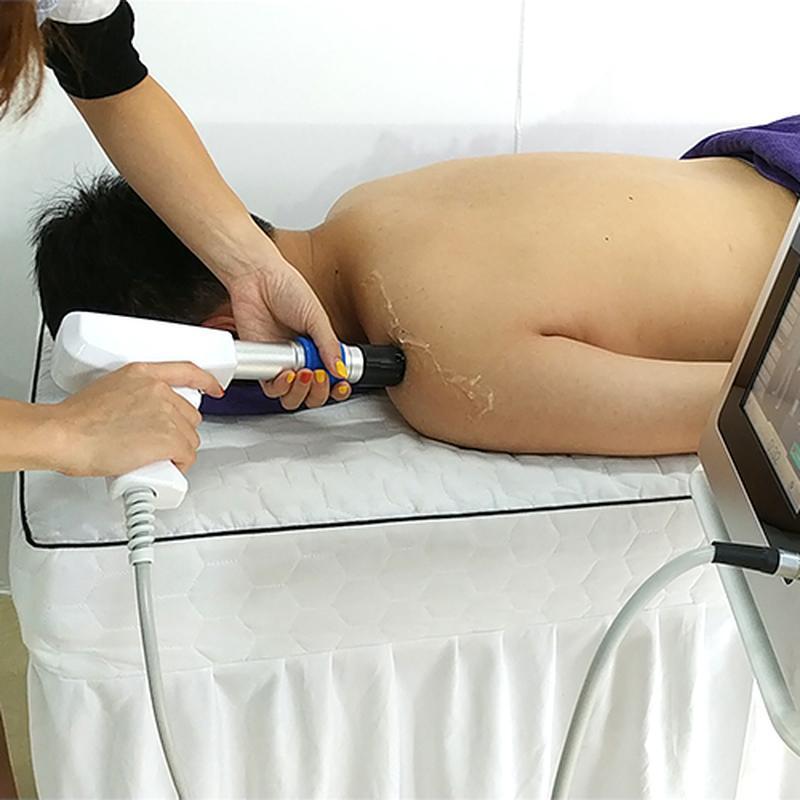
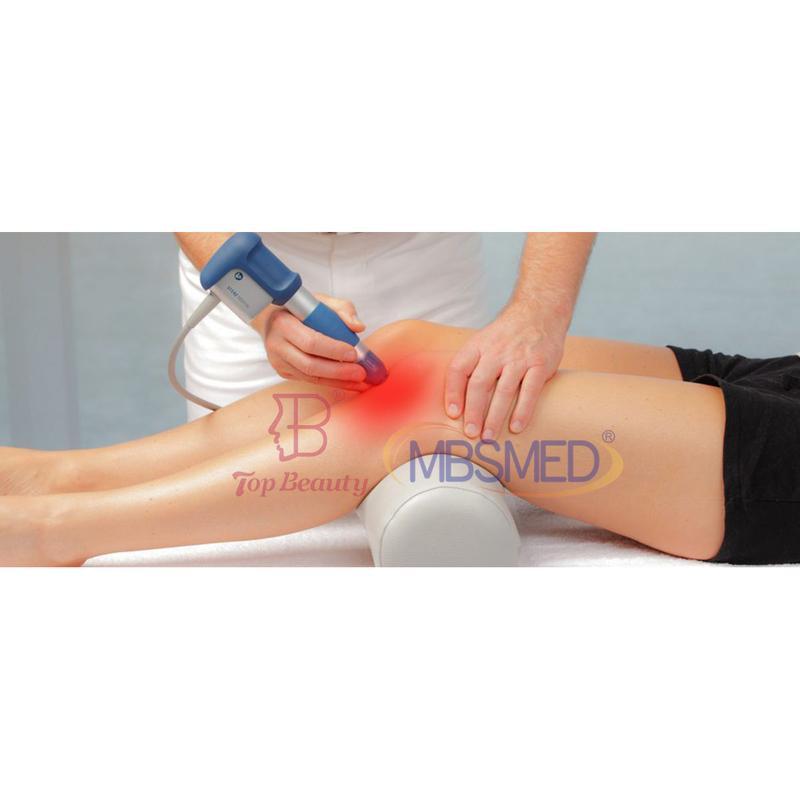
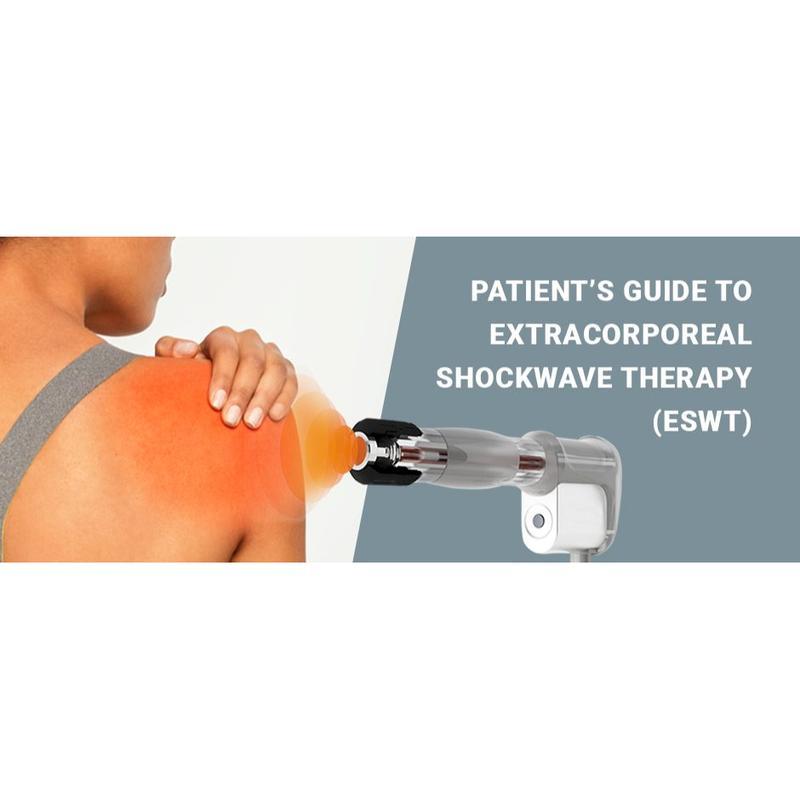
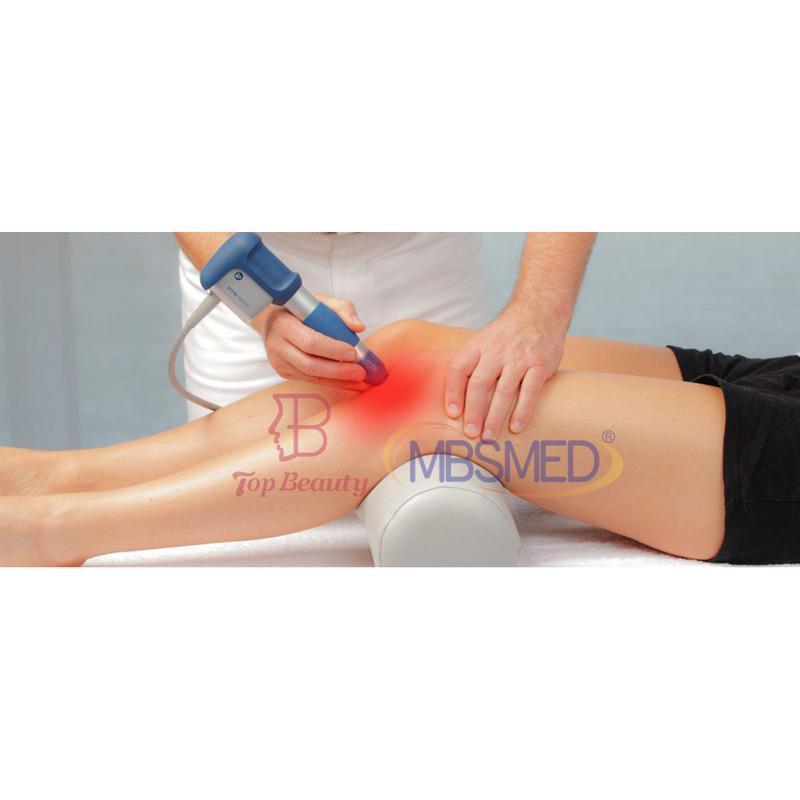
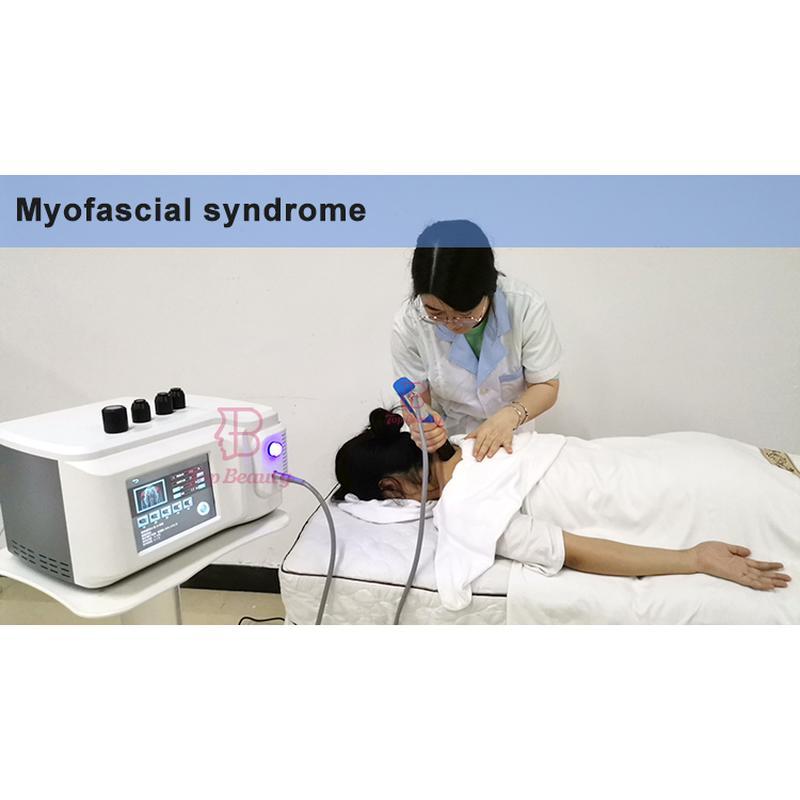
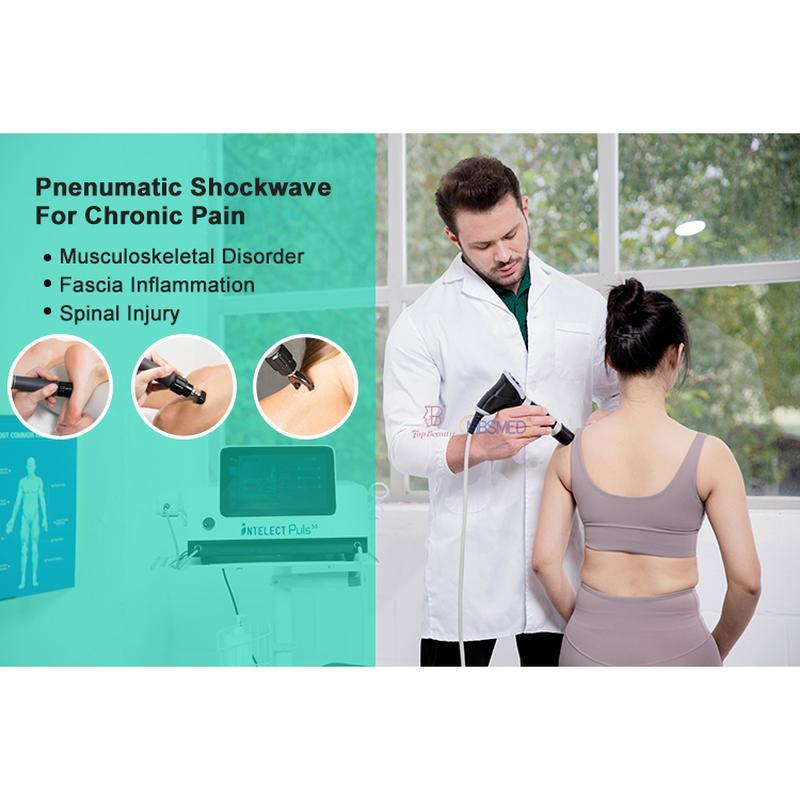
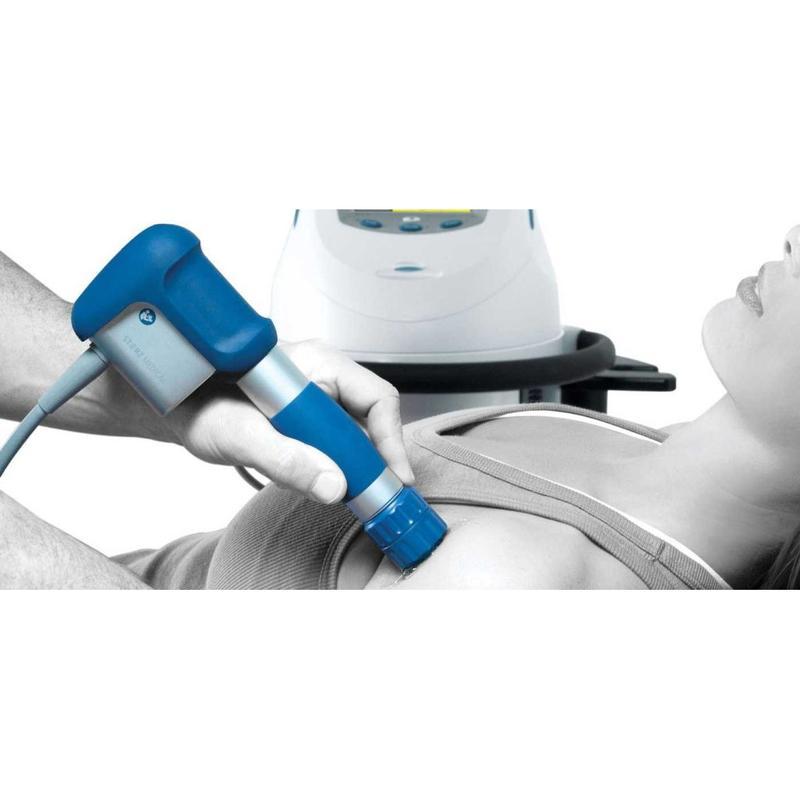
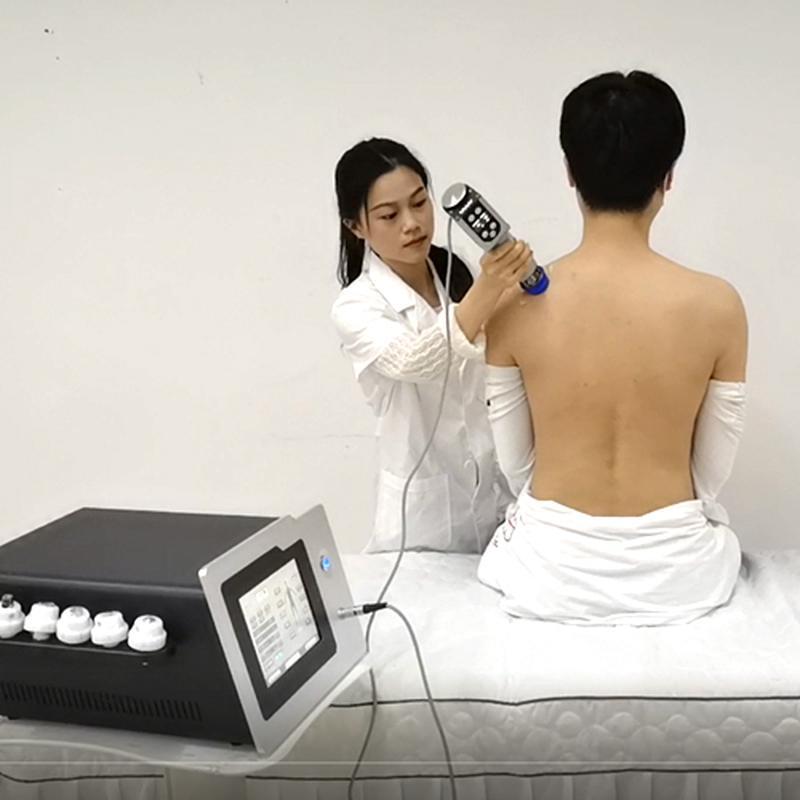
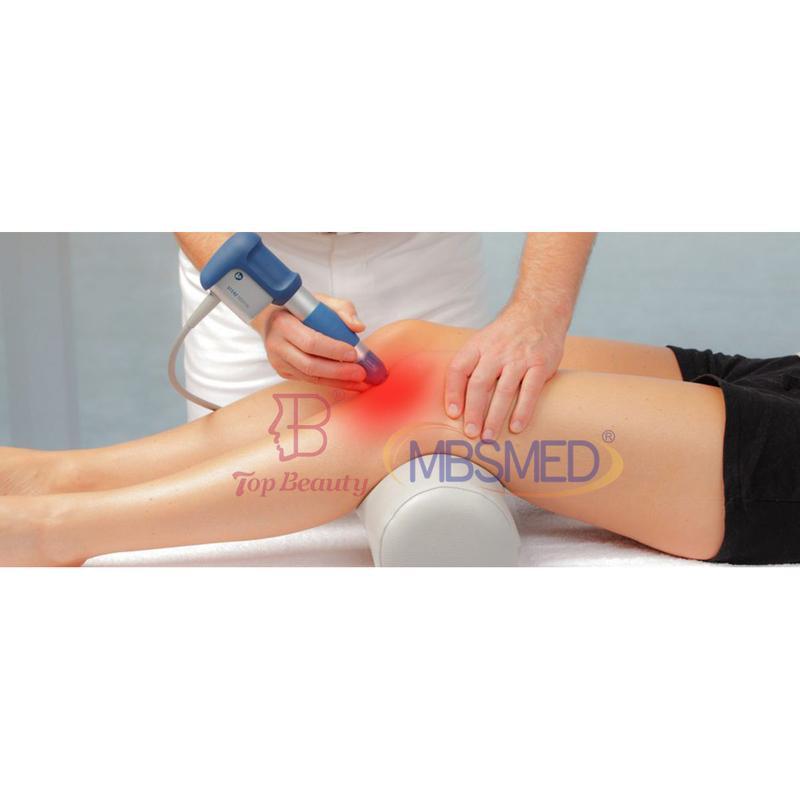
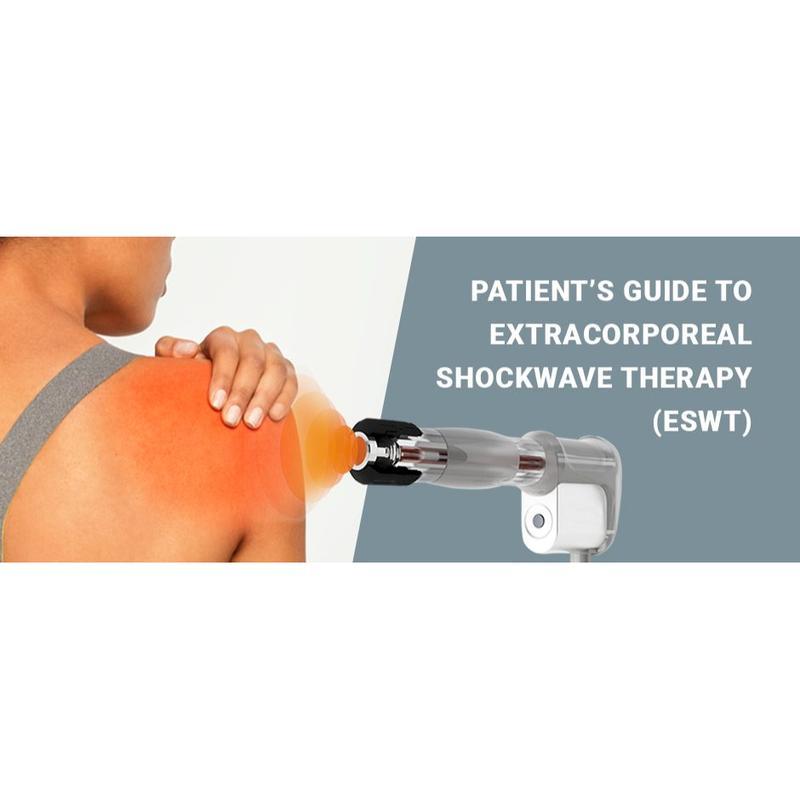
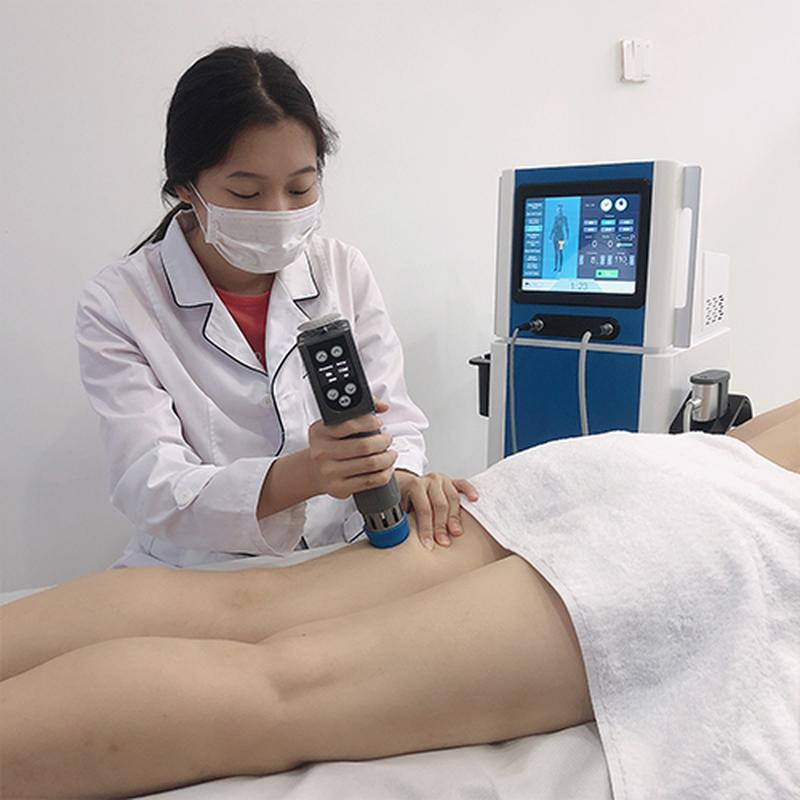
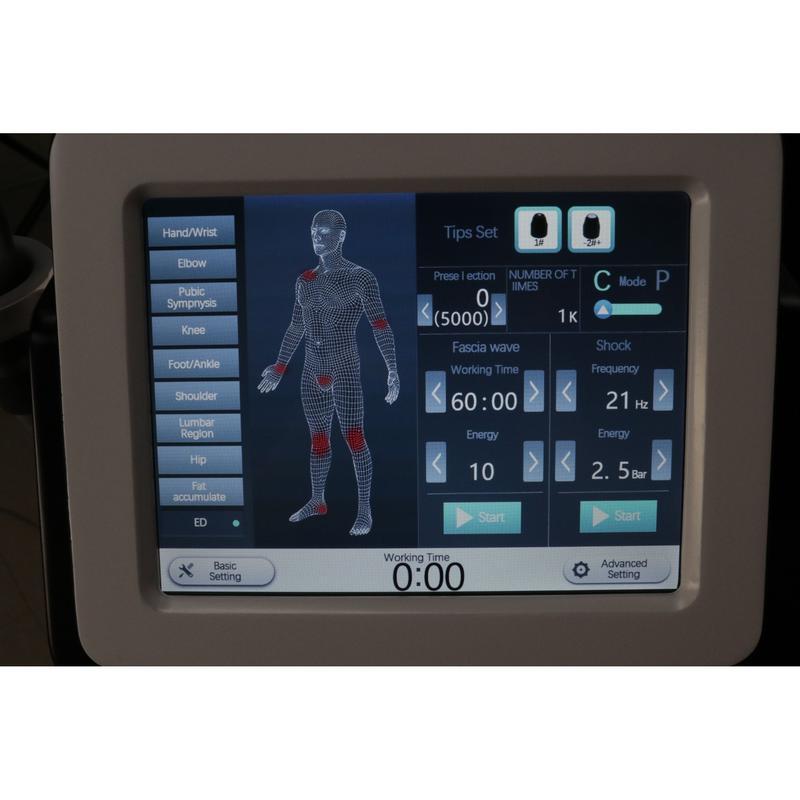
Shockwave Therapy is a non-invasive medical treatment that utilizes high-energy acoustic waves to stimulate healing in injured or affected tissues.
Shockwave Therapy
Definition & Mechanism
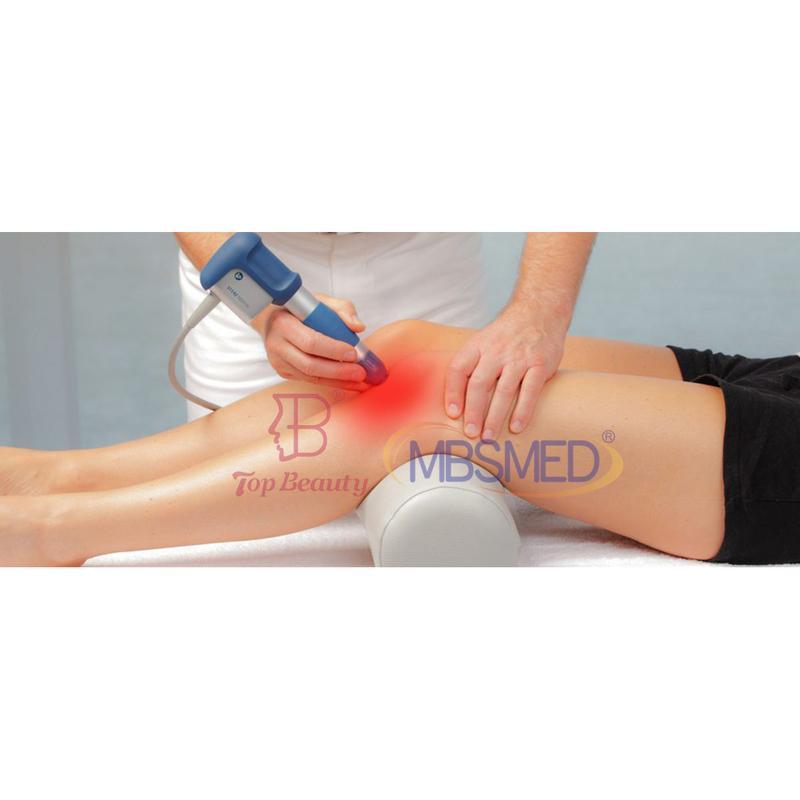
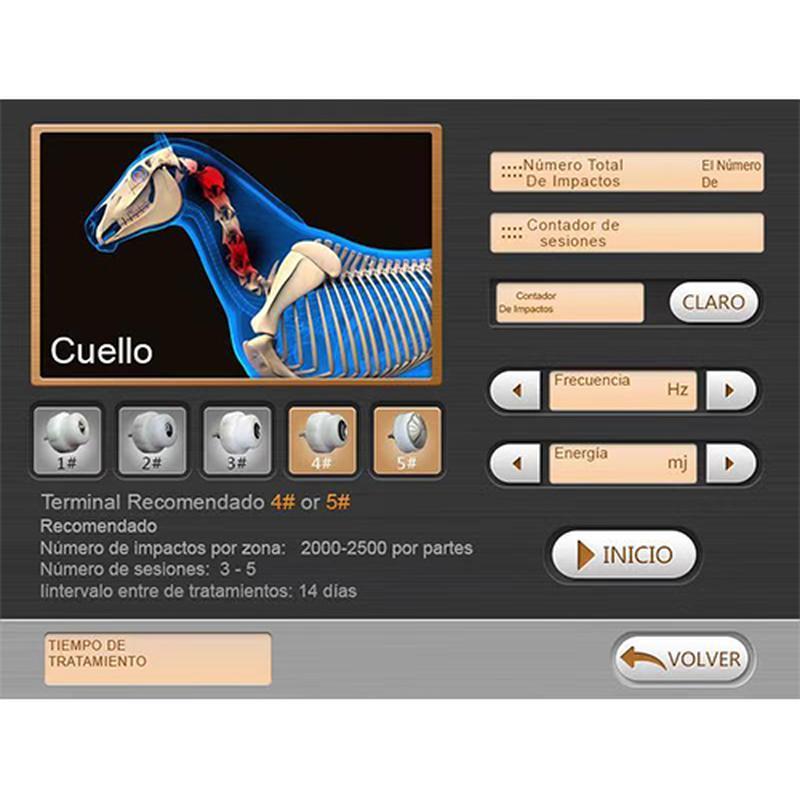
- Acoustic Waves: Delivered via a handheld device, these focused or radial pressure waves penetrate tissues, inducing microtrauma. This triggers the body’s natural repair processes, enhancing blood flow, cell regeneration, and breakdown of calcified deposits.
Types
- Focused Shockwave Therapy (FSWT): Targets deeper tissues with precision (e.g., kidney stones via lithotripsy, chronic tendon injuries).
- Radial Shockwave Therapy (RSWT): Broader, superficial application for conditions like muscle strains or plantar fasciitis.
Common Uses
- Musculoskeletal: Plantar fasciitis, Achilles/calcific tendonitis, tennis/golfer’s elbow, non-healing fractures.
- Urological: Erectile dysfunction (ED) by improving vascular function.
- Other: Emerging roles in wound healing and sports injury recovery.
Procedure
- Duration: 15–30 minutes per session, typically requiring 3–5 sessions.
- Process: Gel is applied to the skin; a device delivers shockwaves. Mild discomfort may occur, but anesthesia is rarely needed.
Benefits
- Non-invasive, outpatient procedure.
- Minimal downtime; most resume activities immediately.
- Avoids surgery risks; effective for chronic conditions.
Risks/Side Effects
- Temporary pain, redness, or bruising.
- Contraindications: Pregnancy, blood thinners, infections, or tumors in the treatment area.
Effectiveness
- Supported by studies for conditions like plantar fasciitis and ED, though results vary. Not universally effective; success depends on individual factors.
Considerations
- Insurance coverage varies; often self-paid for off-label uses (e.g., ED).
- Consultation with a specialist is recommended to assess suitability.
Conclusion
Shockwave Therapy offers a promising, low-risk option for diverse conditions, leveraging the body’s healing mechanisms. While evidence supports its efficacy in specific cases, outcomes depend on proper patient selection and condition severity.